Consistent Hashing Visualizer
I built an interactive visualizer to show how consistent hashing works in distributed systems. Watch keys redistribute as you add or remove servers, and see why databases like DynamoDB and Cassandra use this algorithm.
Demo: consistent-hashing.vercel.app
Source: github.com/brianhliou/consistent-hashing
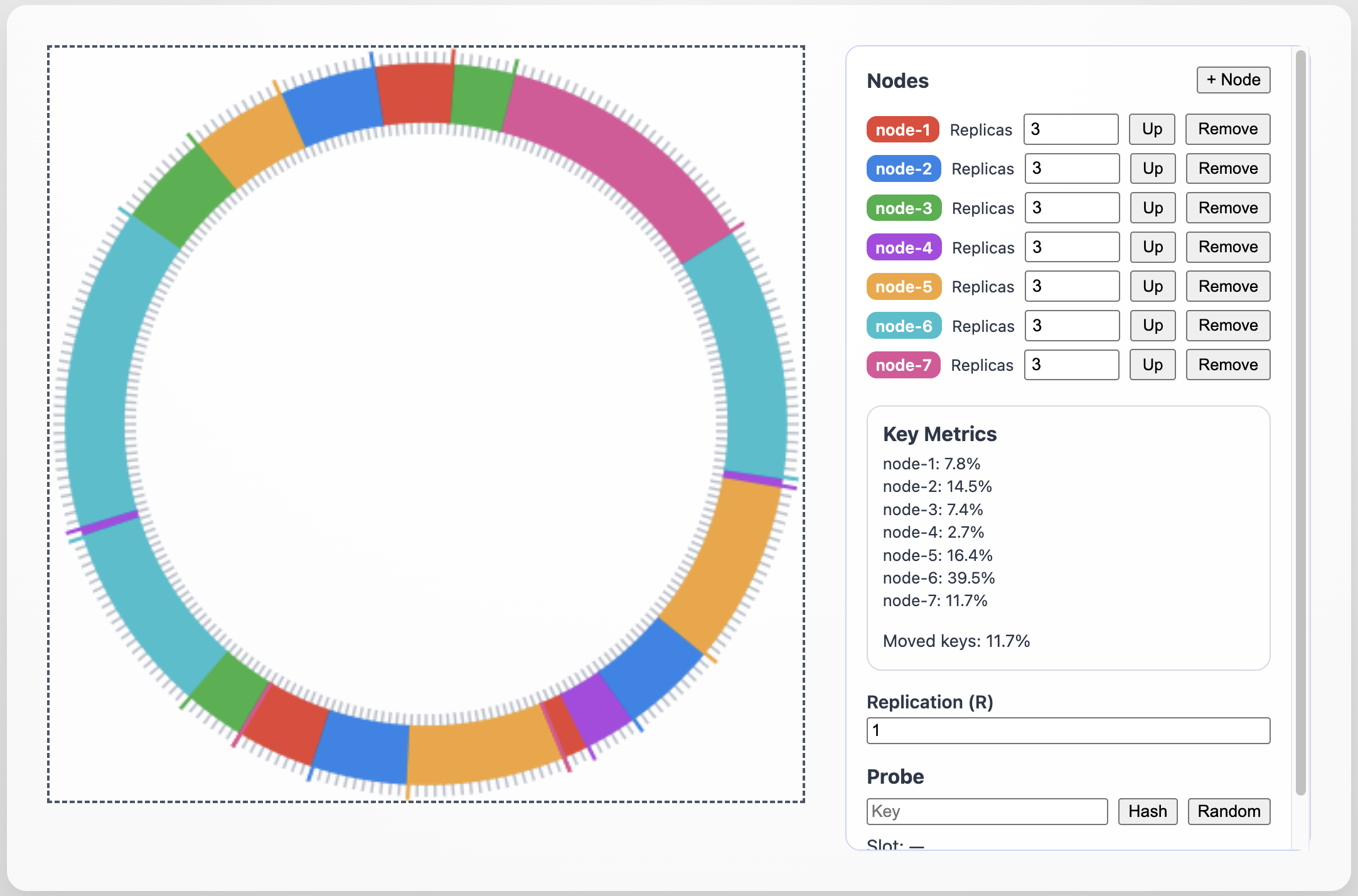
How It Works
The problem: The naive way to distribute keys across N nodes is owner = hash(key) % N. But if N changes, almost every key remaps. Add one node to four? You reshuffle nearly 100% of your keys.
The solution: Consistent hashing fixes this by hashing both keys and nodes onto the same ring. A key is owned by the first node clockwise from its hash slot. When a node is added or removed, only the keys in its immediate arc move.
Implementation details:
-
Ring of slots - We use 256 slots as a toy universe. Each slot is an angle on a circle.
-
Virtual nodes - Each physical node is placed multiple times (replicas) on the ring. More replicas = smoother distribution of key ranges.
-
Lookup - To place a key, hash it to a slot and walk clockwise until you hit a live node. For replication factor
R>1, continue walking to collectRdistinct nodes. -
Movement metric - When the ring changes, we recompute owners for all slots and count how many changed. This illustrates the 1/(N+1) property: adding a node moves about that fraction of keys.
Features in the Demo
-
Ring visualization
256 ticks drawn as a circle. Arcs colored by which node owns that slot. Replica positions marked. - Controls
- Add/remove nodes
- Change virtual node count per physical node
- Toggle node health (simulate failures)
- Adjust replication factor
-
Probe
Enter a key, hash it, and see its primary and secondary owners highlighted. - Metrics
- Per-node share (%)
- Max/mean load ratio
- % of keys moved since last change
- Compare mode
Toggle between consistent hashing and naive modulo hashing to see how much more movement modulo causes when nodes change.
How It’s Built
- Stack: Vite + TypeScript, no heavy frameworks.
- Canvas: for the ring and replicas.
- Plain state object: for nodes, replicas, and ownership array.
- Hash: FNV-1a reduced modulo 256.
This keeps the code short and inspectable. The entire simulation runs in the browser.
Try It Out
Clone the repo, then:
npm install
npm run dev
Visit the local URL to interact with the demo. Run npm run build to produce a static bundle in dist/ that you can deploy to Vercel or any static host.
What to explore:
- Start with 4 nodes and 1 replica each: see the skew.
- Increase replicas to 32: the load balances.
- Add a node: about 20% of slots move.
- Toggle to modulo hashing: nearly 100% of slots move.
- Set replication factor = 3: probe a key, then fail its primary node and watch the secondary take over.
This project is a teaching toy. It’s not optimized or production-ready. But if you’ve ever read about consistent hashing and wanted to “see it happen,” this demo makes the abstractions visible.